Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the idea of calculating maintenance calories and creating a calorie deficit for weight loss with strength training?
As a beginner, these concepts can seem intimidating. That’s why I suggest a simpler approach: eat only homemade food.
By consuming meals prepared by yourself or your family, you can avoid the hassle of counting calories and tracking macronutrients.
Stick to simple, nutritious foods and avoid fried or processed items.
However, if you want to understand calorie counting and nutritional planning, this article will provide valuable insights to help you achieve your weight loss goals through strength training.
How many calories to eat for weight loss with strength training?

There is an ultimate and very easy principle for losing weight which is being in a calorie deficit.
A calorie deficit occurs when you consume fewer calories than your body needs to maintain its current weight.
It is because when you eat fewer calories, your body needs energy to perform the daily tasks, so that energy consumption will go up on the fat stores on your body. Eventually reducing fat from the body.
When calorie deficit paired with strength training, it helps in preserving those precious muscles and making you look leaner with a toned physique. [*]
Recommended Safe Calorie Deficit
Creating a safe calorie deficit for weight loss with strength training is crucial for sustainable weight loss.
Typically the ideal range goes around 500 calories less than your maintenance calorie.
Here’s a breakdown of how to calculate your calorie needs:
- Determine Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): Your BMR is the number of calories your body needs to perform basic physiological functions at rest, such as breathing and digestion. Various online calculators can help estimate your BMR based on factors like age, sex, weight, and height.
- Factor in Activity Level: Multiply your BMR by an activity factor that corresponds to your level of physical activity (sedentary, lightly active, moderately active, very active). This gives you the total calories needed to maintain your current weight.
- Create the Deficit: Subtract 500 to 750 calories from your maintenance calories to establish your target calorie intake for weight loss.
One most important thing is that, if you calculate your calories and say your maintenance calories is 2400, and as we discuss the ideal range for deficit is 500 less calories for weight loss with strength training.
But sometimes our mind thought to go beyond this number and they cut almost half of their maintenance calories, which can lead to a crash diet.
If you follow a crash diet for weight loss, it will end up with nothing. You will crave for junk food and even your body will feel sluggish and weak.
So, create a well-balanced meal for sustainable weight loss.
What is the Optimal Macronutrient Ratio for Losing Weight with Strength Training?
After knowing how many calories you need, it is important to know what to eat in those calories.
That is where macronutrients(Protein, Carbs, Healthy fat) play an important role.
Let’s take it simple, you need only 3 things from your diet which are:
1st is that food products which will help your body to repair after your strength training session, i.e Protein.
2nd that food products which will give your body enough energy to be active whole day after your workout i.e is Complex Carbohydrates
3rd that food products which are the essential building blocks and energy source that fuel your strength training journey i.e Healthy Fats
You only have to play with these types of food only and adjust according to your calories.
For an ideal macronutrients ratio goes like:
- Protein: 25-35% of total calories.
- Carbohydrates: 30-40% of total calories.
- Fat: 20-30% of total calories.
Adjust according to your calories and find out what is your ideal range for these macros.
Now, let’s create a well balanced meal plan.
How Can I Create a Meal Plan that Supports Both Weight Loss and Muscle Gain?
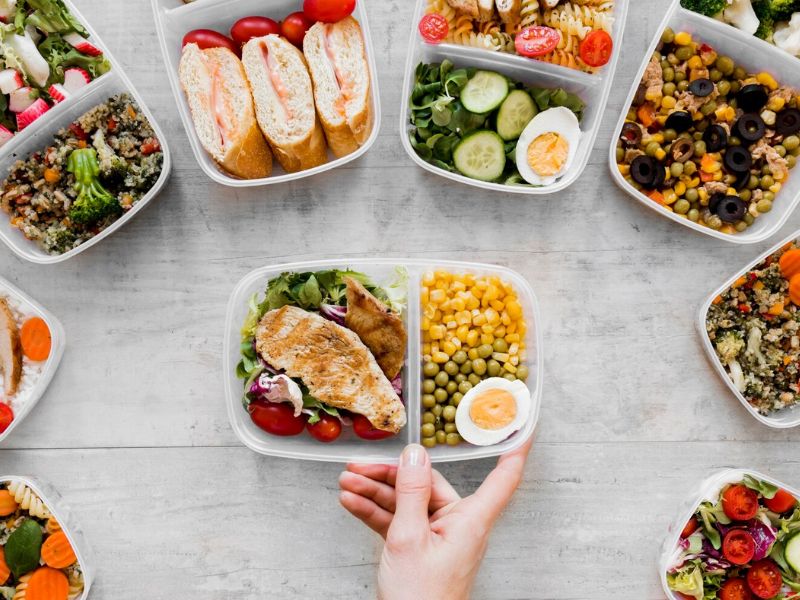

Meal planning is the cornerstone for those looking to lose weight and gain muscle.
- It involves strategically planning your meals in advance to ensure you meet your nutritional needs while supporting your fitness goals.
- It helps you in avoiding unhealthy choices as those meals are already prepped, you will resist going for unhealthy choices.
- It helps you in portion control as their meals are prepared in meal boxes you can buy from online, preventing overeating and aiding in calorie control.
- Having a set meal plan saves time during busy weekdays and reduces the stress of deciding what to eat.
Here is a sample meal plan for weight loss with strength training:
Breakfast:

- Poha
- Upma
- Dosa
- Idli
- Uttapam
- Daliya
- Besan/Moong dal Chilla
Mid-day Snack
- Fruit Salad
- Roasted Chana chaat
Lunch:
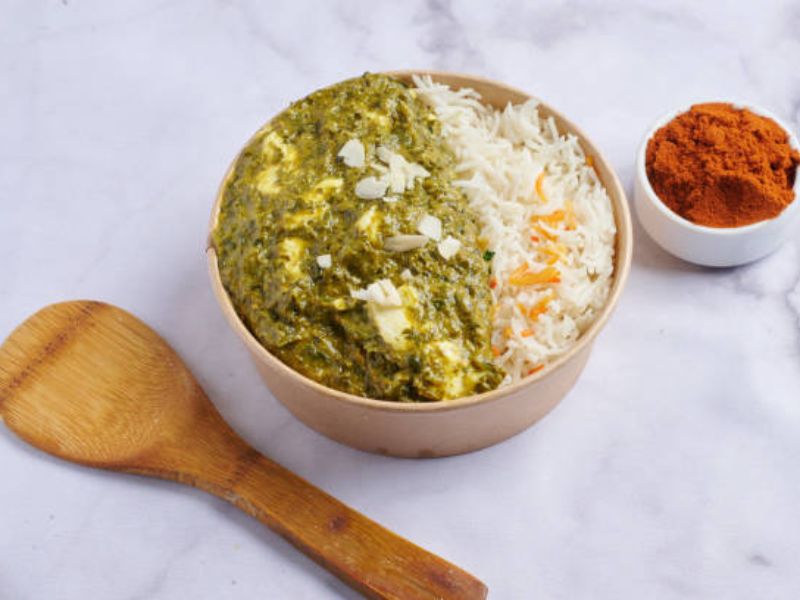

- Vegetable Biryani
- Palak Paneer
- Chicken Curry
- Chana Masala
- Any sort of sabzi which is not fried
Paired it with rice or whole wheat roti.
Pre-workout
- Oats
- Sweet potatoes
- Corn
Dinner:
- Dal
- Paneer Sabzi
- Chicken masala
Preferably paired it with roti at night.
Conclusion
Achieving weight loss with strength training involves a balanced approach to calorie intake and nutritional planning.
By understanding the importance of a safe calorie deficit, typically around 500-750 calories below your maintenance level, you can create a sustainable plan for weight loss.
Avoid drastic calorie cuts to prevent muscle loss and nutritional deficiencies.
Equally important is the optimal macronutrient ratio, focusing on proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
This balance ensures you have the energy for workouts and the nutrients needed for muscle repair and growth.
Planning meals ahead is essential for maintaining this balance, helping you avoid unhealthy choices and control portions.
Remember, consistency and patience are key. Stay committed to your diet and exercise regimen, and adjust your intake as needed on workout and rest days.
For personalized guidance, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist. With these strategies, you can effectively manage your weight loss journey and build a stronger, healthier body through strength training.


12 thoughts on “How Much to Eat for Weight Loss with Strength Training?”